Alumina Smelting
-
Industry:SmeltingEnvironmentMining
-
Processes:Calcination
Industry hurdles we face
Introducing Low-Carbon Alumina Smelting Utilizing microwave
Traditionally, alumina smelting involves converting aluminum hydroxide into α-alumina through calcination at temperatures exceeding 1,000°C. This process is heavily reliant on fossil fuels, making it a primary contributor to CO2 emissions within the alumina smelting process. Reducing CO2 emissions is a major challenge for the alumina smelting industry to achieve carbon neutrality.
We have developed “Green Mining-MX,” an electrification platform for the smelting process that uses microwaves to achieve high efficiency and significantly lower CO2 emissions, and will also contribute to the promotion of economic security.

Results of Screening Tests
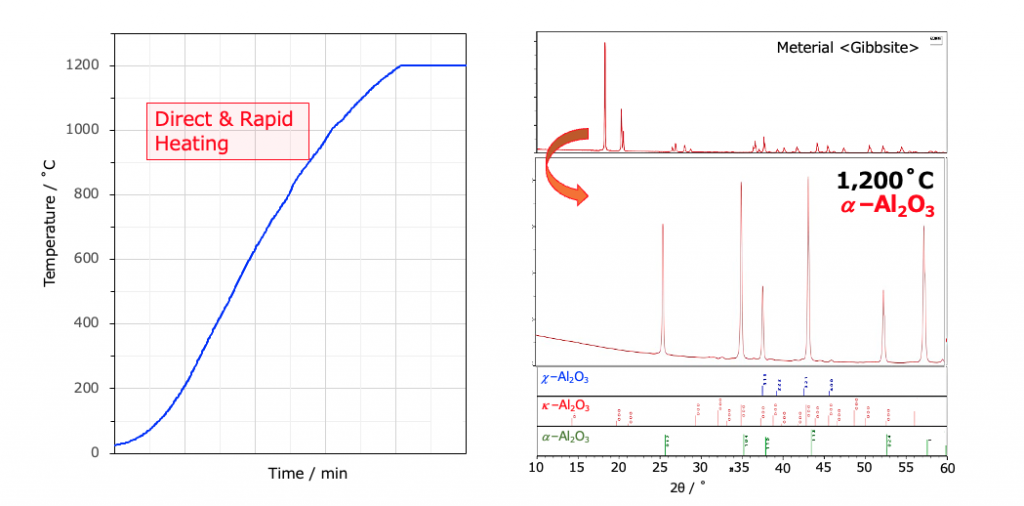
In laboratory tests, it was confirmed that aluminum hydroxide can be converted to α-alumina by microwave heating in a high temperature range. It was confirmed that the temperature can be raised rapidly by direct heating, which is a characteristic of microwaves.
Significance of Using Microwaves
By integrating microwaves with renewable energy sources, we’ve achieved a significant reduction in CO2 emissions.
Future Prospects
Electrifying Alumina Smelting: Paving the Way for a Decarbonized Future
As demand for aluminum is expected to increase in line with the shift to lighter weight automobiles due to EVs, the need for green aluminum, produced through low-carbon refining methods, is more critical than ever.We hope to contribute to the realization of carbon neutrality in the alumina and aluminum industries by providing microwave technology to smelters.
